Emulsão de poliacrilamida catiônica em campo petrolífero
Marca Jiufang
A Origem do Produto Shenyang
O tempo de entrega Prazo de entrega: 7 dias
A capacidade de abastecimento 2000 toneladas métricas por mês
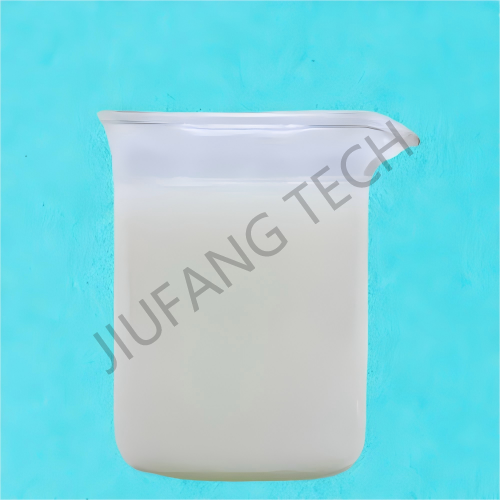
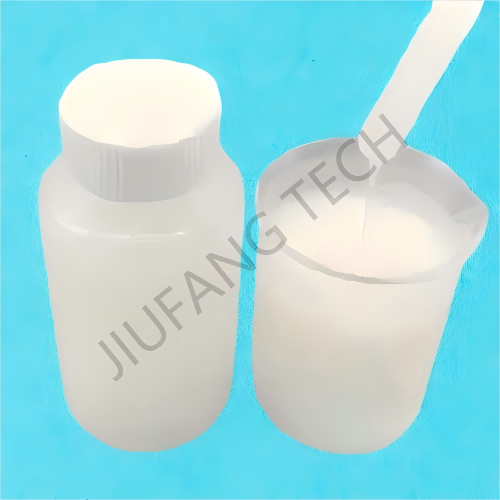
1. PAM catiônico (copolímero de poliacrilamida CPAM) para tratamento de água industrial e doméstica.
2. O copolímero de poliacrilamida CPAM (PAM catiônico) é amplamente utilizado em processos de desidratação em refinarias.
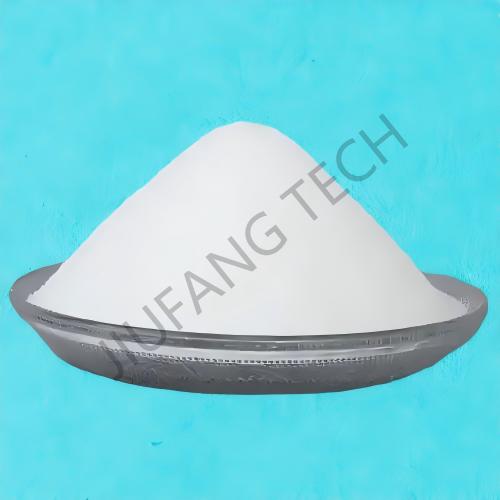
3. PAM catiônico dividido em dois tipos de forma: emulsão e pó.
baixar
Copolymer polyacrylamide CPAM is a kind of multifunctional oilfield chemicals PAM polyacrylamide oilfield treatment agent, which is widely used in various processes of oil exploitation.
Characteristics of Copolymer Polyacrylamide CPAM
1. Multi-monomer copolymerization for designable properties
The core feature of polyacrylamide emulsion copolymer is dddhhhcopolymerizationdddhhh. That is, apart from acrylamide (AM, a hydrophilic and neutral monomer), one or more other monomers are introduced. By adjusting the types and proportions of monomers and the polymerization process, specific functions can be imparted to the polymer.
Common comonomers include:
Anionic monomers: Such as sodium acrylate (AA), 2-acrylamido-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid (AMPS), etc. After introduction, an anionic copolymer polyacrylamide is formed, with the molecular chain carrying a negative charge.
Cationic monomers: Such as acrylamidopropyltrimethylammonium chloride (AMPTAC), methacryloyloxyethyltrimethylammonium chloride (DMC), etc. After introduction, a cationic PAM copolymeric polyacrylamide is formed, with the molecular chain carrying a positive charge.
Other functional monomers: Such as non-ionic monomers (e.g., methacrylamide) or hydrophobic monomers, which can improve the salt-tolerance and hydrophobicity of the polymer.
2. Main types and properties
Based on the charge characteristics of the introduced monomers, copolymeric polyacrylamide emulsion copolymer can be divided into three major categories, with significant differences in properties:
Anionic copolymeric polyacrylamide: The molecular chain contains negative-charge groups such as carboxyl groups (-COO⁻), has good water-solubility, and usually has a relatively high molecular weight (ranging from several million to tens of millions). It mainly exerts its flocculation effect through charge neutralization and adsorption - bridging, and has strong alkali - resistance.
Cationic copolymeric polyacrylamide: The molecular chain contains positive-charge groups such as quaternary ammonium groups, has a strong adsorption ability for negatively-charged colloids (such as organic matter in sewage and sludge), and is superior in dewatering and bactericidal properties. It is suitable for scenarios such as sludge dewatering.
Amphoteric copolymeric polyacrylamide: By introducing both anionic and cationic monomers simultaneously, it combines the characteristics of both, and has stronger adaptability in complex water quality (such as high - salt environments with large pH fluctuations).

Industry-specific attributes:
| Name | Cationic PAM (polyacrylamide emulsion copolymer) | |||
| Application | Polyacrylamide emulsion for oilfield wastewater treatment | |||
| CAS NO. | 9003-05-8 | |||
Other Attributes:
| Appearance | Cationic PAM emulsion | |||
| Solid Content | 48% | |||
| Viscosity Range(ml/g) | 1200~1600 | |||
| Residue | 0.12% | |||
| Insoluble Substance(%) | 0.1 | |||
| Cationic Charge | 80% | |||
| Dissolving Time,min | 40 | |||
| Storage Temperature,℃ | 0~35 | |||
| Shelf Life,month | 12 | |||
Supply Ability:
| Supply Ability | 2000Metric Tons per Month | |||
Lead Time:
| Quantity(kilograms) | 1~50 | >50 | |
| Lead Time(days) | 7 | negotiated | |
















